Hot water safety in health and social care settings
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Hot water is generally an essential building service. Section G3 of Approved Document G defines ‘domestic hot water’ as water that has been heated for cooking, food preparation, personal washing or cleaning purposes. The approved document provides general guidance in relation to hot water supplies. There are also several resources that specifically address hot water safety in health and social care environments.
[edit] Health and Safety Executive guidance
Guidance for the risks associated with hot water and hot surfaces in health and social care premises can be found in the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) Health Services Information Sheet No 6, ‘Managing the risks from hot water and surfaces in health and social care’. This guidance aims to help health and social care providers comply with their legal duties. The information sheet examines the risks vulnerable people may be exposed to when bathing or showering. It also provides guidance regarding places where there are hot surfaces such as pipes or radiators.
Published by HSE, HSG274 Part 2 provides specific guidance for healthcare facilities, care homes and other environments where the population may be susceptible to scalding or burns. This population may include elderly people, people with disabilities or children. Risk assessments can be undertaken to help decision makers evaluate which aspects of the guidance are relevant.
This guidance also includes considerations that could be used to address to Legionnaires’ disease in these settings as well as information regarding water safety groups and water safety plans.
[edit] NHS guidance
The NHS Health Technical Memorandum (HTM 04-01) Safe water in healthcare premises gives guidance on the legal requirements, design, maintenance and operation of hot and cold water supply, storage and distribution systems in all types of healthcare premises. It provides advice and guidance on the control and management of the risk posed by Legionella and other waterborne pathogens that may occur in healthcare settings.
A companion document for Scotland, Scottish Health Technical Memorandum 04-01 Water safety for healthcare premises Part B: Operational management, is also available.
An older NHS Health Guidance Note, “SAFE’ hot water and surface temperatures’, Reference document 34 in Appendix A (published in 1998 and updated in 2013), explains measures that employers should take as part of their duty of care regarding safety measures associated with hot water and hot surfaces. These recommendations are applicable to all healthcare facilities as well as facilities covered under the Registered Homes Act 1984. Some of the recommendations may apply to certain other types of special accommodation where residents could be considered at risk.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- A guide to installing thermostatic mixing valves: what, why and how.
- Approved Document G.
- Care Standards Act 2000.
- Health and Safety Executive.
- Health and safety.
- Hot water.
- Hot water safety.
- HSG 274 Legionnaires' disease, Technical guidance.
- Legionnaires' disease.
[edit] External resources
- HSE, Health Services Information Sheet No 6, Managing the risks from hot water and surfaces in health and social care.
- HSE, HSG274 Part 2.
- NHS, Health Technical Memorandum (HTM 04-01), Safe water in healthcare premises.
- NHS, 'SAFE’ hot water and surface temperatures’ (Reference document 34 in Appendix A).
- NHS Scotland, Scottish Health Technical Memorandum 04-01 Water safety for healthcare premises Part B: Operational management.
Featured articles and news
What they are, how they work and why they are popular in many countries.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
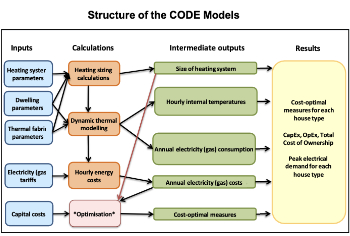
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.
A guide on how children can use LEGO to mirror real engineering processes.
Data infrastructure for next-generation materials science
Research Data Express to automate data processing and create AI-ready datasets for materials research.
Wired for the Future with ECA; powering skills and progress
ECA South Wales Business Day 2025, a day to remember.
AI for the conservation professional
A level of sophistication previously reserved for science fiction.
Biomass harvested in cycles of less than ten years.
An interview with the new CIAT President
Usman Yaqub BSc (Hons) PCIAT MFPWS.
Cost benefit model report of building safety regime in Wales
Proposed policy option costs for design and construction stage of the new building safety regime in Wales.
Do you receive our free biweekly newsletter?
If not you can sign up to receive it in your mailbox here.